Humans have 46, a fly has 8 and an elephant has 56
What am I talking about? Chromosomes
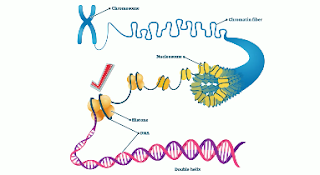
Inside the nucleus of eukaryotic cells is a strand of DNA . DNA is the genetic blueprint and directions for making proteins.The proteins are responsible for traits, such as hair color, height, or eye color. The DNA on chromosomes is arranged in segments called genes which are the instructions for the proteins that create the traits. This strand of DNA is a very long molecule. In fact if you were to stretch it out it would be about five feet in length. During the prophase portion of mitosis this strand of DNA begins to condense and becomes visible.
The DNA begins to coil around histone proteins.
The DNA twists and coils itself and creates a chromosome which looks kind of like an X.
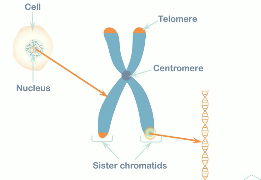
A sister chromatid refers to the identical copies formed by the DNA replication of a chromosome, with both copies joined together by a common centromere. A full set of sister chromatids is created during interphase, when all the chromosomes in a cell are replicated. The two sister chromatids are separated from each other into two different cells during mitosis. During mitosis, the sister chromatids separate into daughter cells, but are now referred to as chromosomes.
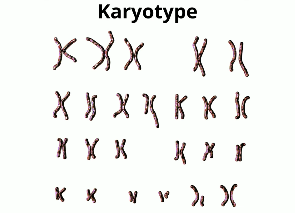
Sometimes you see chromosomes represented as a karyotype.
During the cell cycle of humans the sister chromatids cross over during meiosis and create homologous chromosomes which are two chromosomes in which one is from the male and the others from the female. They have the same genes in the same order but they have different alleles. An allele is a different form of the same trait.
A karyotype is a picture of these homologous chromosomes. Humans have 23 pairs of these homologous chromosomes for 46 total chromosomes other organisms have different numbers and combinations.
Genetics Explained in 3 minutes


0 comments:
Post a Comment