Symbiosis describes a close interactions between two or more different species
There are at least three types of symbiosis, also known as symbiotic relationships.
Mutualism in which both organisms benefit.
Commensalism where one organism benefits and the other organism is neither helped nor harmed.
Parasitism which is when one organism benefits and the other organism is harmed.
Let’s look at some examples of Mutualism.
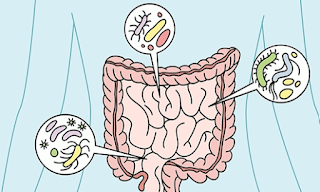
Each person has a personalized collection of bacteria, called the microbiome.These bacteria found in your digestive tract break down carbohydrates and toxins, and help us absorb the fatty acids. The bacteria in your microbiome also help your immune system and manufacturer some vitamins. In return, the bacteria get a place to live and food to eat.
Termites are nature's recyclers, breaking down the cellulose of trees and
decaying wood .Termites cannot digest the cellulose themselves.
Instead they depend on a one-celled protozoa in their stomachs that break down the cellulose into simpler compounds that the termites can use as food.
Yucca moths play an important role in the survival of yucca plants. Without the yucca moth, the yucca plant would lose a very important pollinator, and without the plant, the moth would lose a food source.
Commensalism
Hermit crabs live in shells made and then abandoned by snails. This relationship neither helps nor harms the snails.
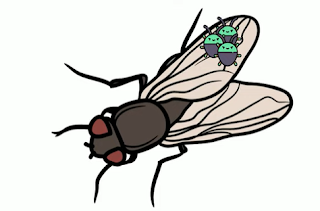
Mites hitch a ride on flies and bees. The mite has a suitable method to grip onto an insect or other animal, and gets transported to another place. A phoretic mite is just a hitch-hiker and does not feed during the time it is carried by its temporary host.
The mites receive transpiration and a place to live and the fly is neither helped nor harmed.
Parasitism
Lampreys are primitive fish with a limited digestive system. They
attach to and feed on the body fluids of fish with more advanced
digestive systems, often leading to the death of the host fish.
This example is bizarre. The fungus Ophiocordyceps unilateralis
uses its spores to infect ants and dramatically changes their behavior. Instead of working normally alongside the colony, these ants leave their nest, high in the trees, and make their way down to the lower leaves. Once there the fungus kills the ant, grows inside the head of the ant to release more spores. Kinda weird




0 comments:
Post a Comment