Year long Review of Life Science
We start the year with the basic unit of life, the cell.
In other words, the cell is considered the smallest thing that is alive.
For something to be alive it needs to have these six characteristics.
- Made of cells,
- Contain DNA
- Respond to stimuli
- Grow and develop
- Reproduce
- Require energy
The organelles in a cell work together to keep the cell alive.
These include,
- The nucleus which is the location of DNA.
- The mitochondria which converts ATP into energy for the cell.
- The ribosomes which create proteins.
- The ER which moves proteins and other materials throughout the cell.
- The Golgi body which transports and repackages proteins and lipids through out the cell using vesicles.
- Lysosomes digest waste material and vacuoles store materials.
Living organisms can be made up of one cell, which are called unicellular, or have many cells, which are called multicellular.
Life also has levels of organization.
Cells make tissues, which make organs which make organ systems, which make organisms.
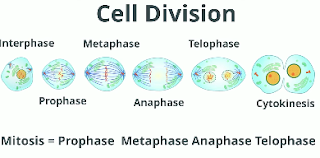
The cell divides during cell division, which includes 6 steps.
Cell division begins during interphase when the cell makes a copy of the DNA.
Mitosis begins with prophase.
During prophase chromosomes first appear. During metaphase, the nuclear membrane
dissolves and the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell.
During anaphase, the sister chromatids separate and move away from each other.
During telophase, the nuclear membrane forms around the chromosomes and the chromosomes uncoil.
This is the end of mitosis.
During cytokinesis, two daughter cells are created.
Genetics is a study of how traits are passed from one generation to the next.
Major Topics of Genetics
Genes are segments of DNA that have instruction for a trait.
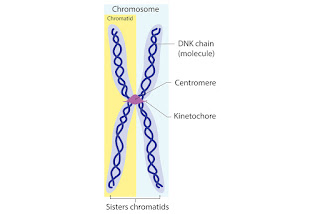
Chromosomes are condensed segments of DNA. A chromosome has two sister chromatids attached by a centromere.
Traits are characteristics like hair color which can be passed to the next generation.
Alleles are different forms of the same trait.
When two organisms reproduce sexually, the offspring is slightly different than the parent.
As a result, the world has a tremendous variety of life.
Charles Darwin proposed the theory of evolution to explain this variety of life.
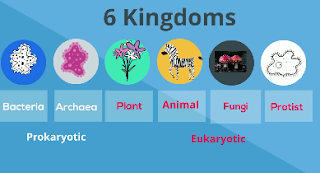
The six kingdoms of life include,
Two kingdoms,bacteria and archaea are prokaryotic, which means they do not have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles, and contain 100% unicellular organisms.
The other four kingdoms are eukaryotes, which means they have a nucleus and include plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
Plants are autotrophic, which means they get their energy from the sun.
Animals and fungi are heterotrophs, which means they depend on other organisms for food and bacteria and protists have both autotrophic and heterotrophic organisms.
A forest is an ecosystem, a pond can be considered an ecosystem, and even a rotting log can be an ecosystem.
An ecosystem is a community of living and non-living objects that live together in a particular area.
Let's look at a cartoon example.
In this ecosystem, you have the living factors called the biotic factors, which include the hawk, the bear, fish and all other living organisms together with non-living factors called abiotic factors such as water, sunlight, and temperature.
All of these factors interact to form a community.
Ecosystems come in a wide variety of sizes.
It may exist in a smaller area, such as a decaying tree trunk or a pond, or it can exist in large forms, like an entire rainforest.
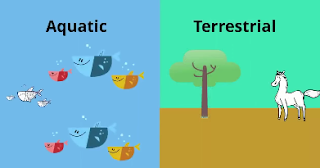
Two main types of ecosystems are terrestrial and aquatic.
A terrestrial ecosystem is a community found on land consisting of organisms and the interactions of the biotic and abiotic components in a given area.
An example would be a deciduous forest. An example of an aquatic ecosystem would be a a lake, river, or a coral reef.
Within these ecosystems, you have symbiotic relationships.
Among living factors there are three main types of symbiotic relationships.
Mutualism occurs when both species benefit, for example a bee obtains nectar
from a flower and spreads pollen on the flower which helps the flower reproduce.
Commensalism implies that one species benefits while one is neither helped nor harmed.
A clownfish gets protection from sea anemone and the sea anemone gets nothing in return.
A parasitic relationship is one in which one benefits and the other is harmed.
A tick gets tasty meal from a human, while the human is harmed and may get sick.
The more you study how life on our planet works, the more surprising and interesting it becomes.
You may Enjoy...





0 comments:
Post a Comment