If you take a look at most drawings of a cell and the cell organelles a major component is usually missing. The cytoskeleton.
As the name implies it is the skeleton of the cell.
The cytoskeleton of a cell is a network of filaments running throughout the cell.
It provides tracks or highways for the movement of vesicles and other objects in the cell, helps pull the chromosomes apart during mitosis and even helps the cell move. Some single cell organisms move using cilia made up of cytoskeleton filament.
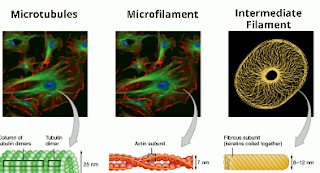
The cytoskeleton consists of three types of fibers, microfilaments, intermediate filaments,and microtubules.
Microfilaments are fine, thread-like protein fibers. They are composed predominantly of a protein called actin these filaments create service highways for the vesicles that need to be moved in the cell and may hold organelles in place.
Intermediate filaments are medium in length and they help maintain the shape of the cell
For example a red blood cell has a unique donut shape cytoskeleton filaments help produce this unique shape.
Microtubules are the largest filaments and also create tracks for proteins.
Think of the microtubules as roads in the cell They also help pull the chromosomes apart during mitosis.
Microtubules also help with the movement of the entire cell by helping to create flagella or cilia that helps propel certain cells.



0 comments:
Post a Comment