I enjoy most vegetables, but Brussel sprouts are very bitter tasting to me.
Why do Brussel sprouts taste very bitter for some people but not for others?
One type of taste receptor tastes for a bitter chemical. This PTC receptor is coded by a gene.
As a result for some people like me, Brussel sprouts taste very bitter. For others, they do not.
Let’s figure out what is going on genetically in very basic terms and this interaction between genes and alleles.
Genes are portions of DNA that contain the code for a particular characteristic called a trait. For example, this portion of the DNA may code for height in a pea plant or this portion may code for the color of the flower of a pea plant.
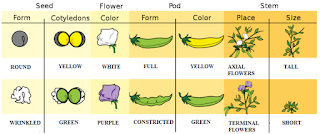
A trait is a characteristic that can be passed from one generation to the next like the color of these apples. Gregor Mendel, who is considered the father of genetics, studied seven traits of pea plants.
notice that for each trait there are different forms, for example, the color of the flower can be white or purple the pea plant can be tall or short for all seven traits each trait has a different form these would be examples of alleles, different forms of the same trait.
Remember, an allele is a different form of the same trait back to the pea plants
The seed can be round or wrinkled or take the form of full or constricted.
The pea plants received half of the genetic information from the male and half from the female.
Each parent contributes an allele.
Together with the two alleles you inherit determine the type of trait you inherit.
The allele can be either dominant or recessive,
The Dominant allele is represented by a capital letter. A dominant allele will cover up or mask a recessive allele. You must inherit two recessive alleles represented by a lower case letter to express a recessive trait.
So in summary, a gene is a portion of DNA that codes for a particular trait.
Traits are characteristics that can be passed from one generation to another
and alleles are different forms of the same trait.



0 comments:
Post a Comment