When you eat a slice of pizza you are transferring energy from the sun. This may surprise you but the sun is the original source of energy for your body.So let’s take a look at the difference between an autotroph that gets energy directly from the sun and a heterotroph that gets energy indirectly from the sun from other sources, like a pizza.
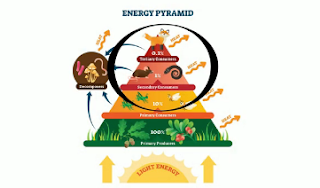
All plants and other organisms that produce their own food in an ecosystem are called autotrophs or self feeders.
An autotroph is an organism that collects energy from sunlight or inorganic substances to produce food.
Where there is no sunlight some organisms like giant tube worms use bacteria found inside them and then oxidize hydrogen sulfide, add carbon dioxide and oxygen, to produce sugar, sulfur, and water.
Autotrophs are also called producers.
Autotrophs are the foundation of all ecosystems.
They are also called consumers.
A heterotroph that eats only plants is called a herbivore.
Heterotrophs that eat other heterotrophs are called carnivores. Examples would include lions and wolves.
Examples includes bears and humans.
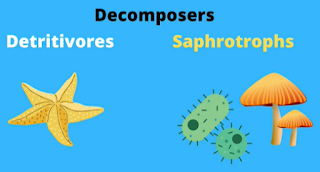
Decomposers like bacteria and fungi are also classified as heterotrophs. They play a very important role in an ecosystem because they recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Two types of decomposers are detritivores which eat fragments of dead matter. Examples include worms, dung flies, sea cucumbers, and sea stars.
Saprotrophs are organisms that feed by absorbing dead organic matter. Most saprotrophs are bacteria and fungi.
Anytime you see something rotting like this log you know a saprotroph is hard at work.
Types of Natural Selection











.png)