In 1855, Rudolph Virchow, a German scientist, discovered that all cells come from other cells. How do cells produce more cells? Cells go through a carefully regulated process called the cell cycle that consists of two main phases: interphase and mitosis. At the end of the cell cycle, the original cell splits, resulting in two daughter cells. Today, we will focus on mitosis. We will learn about the four steps of mitosis and what occurs during each. Mitosis occurs after interphase.
Interphase is the first phase of the cell cycle in which cells grow, replicate their DNA, and make sure they are healthy and ready to divide. It is the longest phase in the cell cycle.
1) Chromatin (genetic material containing DNA, RNA, and proteins) condenses into threadlike structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are x-shaped, and have left and right “arms” (sister chromatids) that are joined in the center by centromeres.
2) Centrosomes are organelles that act as the cell’s organizer during mitosis. During prophase, centrosomes separate and move toward opposite ends of the cell.
3) The centrosomes begin to produce threads called spindle fibers. These spindle fibers will attach to the chromosomes and move them around during the other steps of mitosis.
4) The membrane (or envelope) around the cell’s nucleus dissolves. This is what gives the centrosomes’ spindle fibers the ability to attach to the chromosomes.
In summary, cells multiply by making copies of themselves during the cell cycle. There are two main phases of the cell cycle: interphase and mitosis.
Cells grow and make copies of their DNA during interphase. After double checking to make sure it completed interphase properly, the cell moves into mitosis.
Mitosis consists of four main steps: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. At the end of mitosis, division of the cytoplasm, or cytokinesis, occurs. You now have two cells with identical genetic material.
Here are some tricks to help you remember this information:
*The latin prefix “pro” means “before”. Prophase occurs before all the other steps in mitosis.
*During metaphase, the chromosomes align in the center of the cell. Think “m” in metaphase for “middle” of the cell.
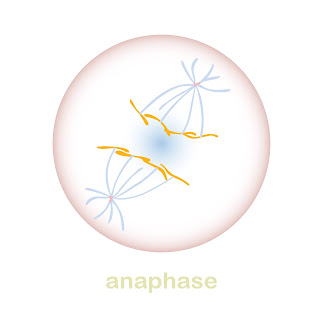
*During anaphase, the sister chromatids are pulled away from each other. Think ‘a’ in anaphase for “away”.
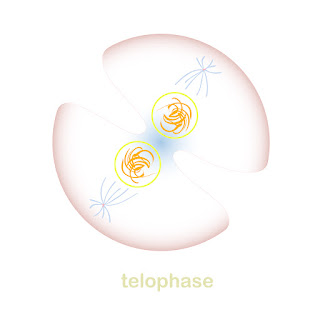
*During telophase, the recently separated sister chromosomes are on opposite ends of the cell from one another, and they live inside different houses (nuclei). The chromosomes now need a “telo”phone to communicate with each other.
*You can use the acronym “PMAT” to help you remember which order the steps occur in.
Relevant links:





0 comments:
Post a Comment